Looking Ahead to 2025: Cybersecurity Trends and the FAIR Institute’s Plans for the Future


Now that we’ve stepped into 2025, let’s take a look at what’s in store for cyber risk quantification and management this year. It’s always hard to predict what will happen in the coming year, but we already see that organizations continue to grapple with AI-driven risks, new compliance mandates, an increasing focus on resilience, and a global talent shortage in cyber risk management.
At the FAIR Institute, we see these challenges as opportunities to strengthen the science of quantitative risk management, equipping professionals with the tools, frameworks, and community support they need to thrive.
Todd Tucker is Managing Director of the FAIR Institute
Cybersecurity Trends and Challenges Impacting Cyber Risk Management
Before we discuss what’s on the FAIR Institute’s agenda for 2025, let’s examine trends impacting the cyber risk management profession.
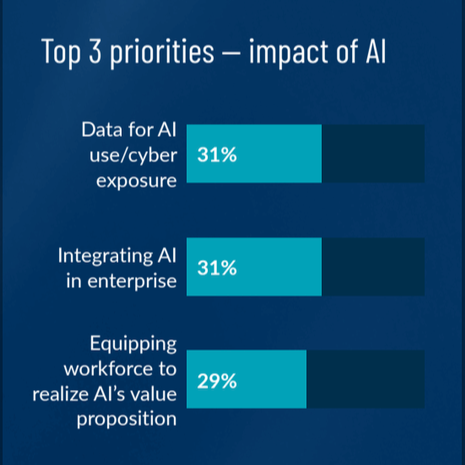
Artificial Intelligence
As I mentioned in my blog post looking back at 2024, AI is reshaping cybersecurity in profound ways, offering both opportunities and threats. This trend will continue and likely become more pronounced in 2025.
For cyber risk professionals, AI introduces dynamic risk profiles that require sophisticated modeling to assess the frequency and magnitude of potential loss events. We anticipate that threat actors will increasingly embrace GenAI to exploit human vulnerabilities using more sophisticated phishing attacks, fake videos and voices, and other techniques. Threat managers should pay close attention to these developments and train employees, partners, and customers to be more aware of the threats.
Cyber risk managers should pay close attention as well, and create or update their risk scenarios accordingly. Using a cyber risk management system (CRMS) that automatically incorporates updated threat and controls data will help stay on top of new developments.
Using a FAIR-Based Risk Approach to Expedite AI Adoption at Your Organization
AI will also have a greater impact on those systems and cyber risk processes as well. Based on our work with technical advisor Safe Security and talking to other vendor professionals in the field, it’s clear that solution providers are increasingly using AI to enhance processes such as ingesting control assessment questionnaires with natural language processing, analyzing asset data and other feeds, processing threat intelligence, and performing predictive analytics.
Of course, cyber risk management data source providers, i.e., those vendors that provide cybersecurity controls (especially Loss Event Controls and Variance Management Controls), are increasingly using AI to bolster the capabilities of their products. In turn, this will in turn improve the CRMSs that consume those data sources.
European Regulations: DORA and NIS 2
Two major regulatory frameworks in the European Union—the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and the NIS2 Directive (EU 2022/2555)—will begin to significantly impact enterprises in many European countries in 2025. The former was enacted with an entry into force date in 2023 and an application date of January 17, 2025; the latter’s entry into force date was 2022 and EU Member States were required to transpose the directive into national law by October 17, 2024. As a result of these dates and various delays, legal experts expect these laws to impact organizations in many large European countries, such as Germany, France, The Netherlands, Austria and more, in 2025.
Both regulations emphasize formalized risk management approaches, resilience, and robust incident reporting.
- DORA: Financial institutions must adopt structured risk management frameworks and evaluate third-party risks while meeting strict incident reporting requirements. They must also implement controls to improve resilience.
- NIS2 Directive: Updated to include governance, supply chain risk management, and resilience, the framework encourages the adoption of formal risk assessment methodologies, aligning closely with FAIR.
While these frameworks allow for both qualitative and quantitative risk management approaches, the adoption of FAIR helps satisfy their requirements with a formal, standards-based, industry-proven approach. Indeed, these regulatory changes emphasize the need for quantitative methods to:
- Measure inherent and residual risks.
- Demonstrate the financial and operational impact of cyber incidents.
- Assess third-party and supply-chain vulnerabilities.
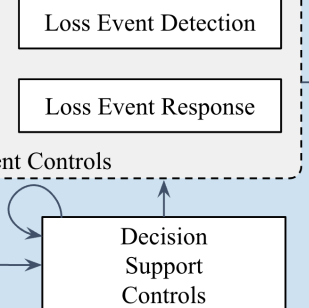
Our models—FAIR, FAIR-CAM, and FAIR-MAM—are very well suited to helping organizations meet these mandates and build stronger, more resilient risk management programs.

FAIR-CAM overview from the FAIR Framework white paper
The Renewed Focus on Resilience
Cyber resilience—the ability to recover from disruptions quickly and minimize their impact—is taking center stage in 2025. This focus reflects that prevention alone is no longer sufficient in the face of increasingly sophisticated threats.
As per the regulatory frameworks above, resilience is also driven by mandates. But given the impacts of outages on businesses— lost revenue, reputational harm, and legal liability—resilience has become an essential outcome for those not subject to those regulatory requirements.
This is where FAIR is so helpful. As a quantitative risk management framework, FAIR helps organizations:
- Conduct scenario analyses to prepare for worst-case events based on their business impact.
- Prioritize investments and understand the return on investment (ROI) in controls that enhance recovery and continuity.
- Extend resilience strategies to include third-party dependencies and supply chains.
Incident reporting requirements under DORA and other frameworks further underscore the importance of resilience, encouraging organizations to model the cascading effects of incidents and plan for systemic risks.
Third Parties as Part of the Attack Surface
Regulators around the globe are placing increased emphasis on third-party cyber risk, reflecting the growing recognition that a company’s attack surface extends beyond its own perimeter. Frameworks such as the NIS2 Directive and DORA, described above, and the SEC cybersecurity rules require organizations to assess and mitigate risks posed by their vendors and other third-party service providers.
This shift is driven by high-profile breaches where attackers exploited vulnerabilities in third-party systems to compromise primary targets. As supply chains become more interconnected and reliance on external service providers grows, regulators are demanding that companies take a more proactive stance in managing the security risks of their partners.
To meet these demands in 2025, companies must adopt a mindset that treats third-party services as an integral part of their own attack surface. Effective third-party risk management (TPRM) programs include conducting thorough due diligence, requiring regular security audits, and integrating vendors into incident response planning.
FAIR can further help organizations evaluate the financial impact of third-party risks and prioritize mitigation strategies. By treating third-party security as a core component of their cybersecurity strategy, organizations can not only achieve regulatory compliance but also build resilience against the ripple effects of supply chain cyber incidents.
 BCG Talent Shortage Report
BCG Talent Shortage Report
The Cyber Risk Management Talent Gap
One of the biggest challenges that businesses face in 2025, as they’ve faced in the years before, is a large cybersecurity talent shortage. Indeed, this challenge is highlighted in a recent research report by BCG in October 2024 (image above) that revealed a “critical global cybersecurity workforce shortage of 2.8 million professionals” and that “59% of CISOs say workforce shortage is a ‘top barrier for achieving their security posture.’” The authors anticipate that this gap will be “the key factor behind more than 50% of significant cybersecurity incidents worldwide.”
The report looked deeper into the types of roles (read, skills) for which shortages exist. Ranking sixth (among 17) roles is Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), with 38% of the more than 6,000 respondents reporting a gap. The good news: eight (8) percent reported that they’re working to close the gap.
As the demand for cyber risk management increases, the skills gap means that businesses will have to find ways to be more productive with their resources. This will translate into training and skills development and investments in processes and tools. We expect to see an emphasis on both in 2025.
The FAIR Institute’s Plans for 2025
In response to these challenges, the FAIR Institute is launching several strategic initiatives to empower cyber risk professionals and advance the practice of quantitative risk management:
 FAIR Cyber Risk Management Framework overview
FAIR Cyber Risk Management Framework overview
Expanding the FAIR Cyber Risk Management Framework
We recently introduced the FAIR Cyber Risk Management (CRM) Framework, integrating the FAIR Model, FAIR-CAM, and FAIR-MAM. This comprehensive framework helps organizations measure, manage, and communicate risk effectively. In 2025, we will begin expanding upon Framework with the FAIR Cyber Risk Management Body of Knowledge™ (CRMBoK™), an online resource that will address:
- Best practices for implementing and operating effective CRM programs;
- How to organize and staff for CRM and integrate with enterprise risk management programs;
- How to identify, prioritize, and build risk scenarios;
- Common data sources and their roles in FAIR cyber risk management;
- How to use the FAIR-CAM to understand the impact of controls on cyber risk;
- How to use the FAIR-MAM to estimate cyber losses;
- How to use FAIR to perform cyber investment planning and measure ROI; and
- How to build and execute risk treatment plans.
The CRMBoK will serve as an invaluable resource for cyber risk professionals who are building or maturing their programs, especially given the talent gap.
Launching the State of Cyber Risk Management Research Program
Kicking off in Q1, the FAIR Institute will launch the State of Cyber Risk Management Research Program. This will comprise primary and secondary research to:
- Measure and analyze the maturity and outcomes of CRM programs across industries;
- Correlate maturity with metrics like reduced loss frequency and improved financial performance;
- Identify trends and gaps to guide the evolution of cyber risk management practices.
This State of Cyber Risk Management will provide valuable benchmarks for organizations looking to align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.

FAIR Institute Head of Executive Education Bernadette Dunn and Director of Membership and Programs Luke Bader promoted FAIR education at RSAC24
New Education and Certification Programs
Education has always been central to our mission. As I described in an earlier blog post, we will launch new Cyber Risk Management training and certification options to:
- Train professionals to apply the FAIR CRM Framework and the CRMBoK.
- Provide certifications that validate expertise in quantitative risk management.
- Support career development for the next generation of cyber risk leaders.
We anticipate this training will span six different courses, from FAIR Foundations and FAIR Cyber Risk Analysis to FAIR Cyber Risk Strategy. Those will support the attainment of three different professional certifications (e.g., FAIR Certified Cyber Risk Analyst™, FAIR Certified Cyber Risk Leader™, and FAIR Certified Cyber Risk Executive™). We aim to help CISOs and Chief Risk Officers better address the talent and skills shortages they face.
Strengthening Collaboration and Community
We are also hard at work to provide more opportunities for our community of more than 16,000 members to engage with one another, share their knowledge and expertise, and grow their networks. We’ll be announcing the save-the-date for the 2025 FAIR Conference (in New York City), our 2025 European FAIR Summit (in London), and our 2025 Asia-Pacific Summit (in Sydney).
We’re also in the process of announcing our schedule of local chapter meetings. We hope to introduce new chapters in 2025 to allow more members to engage with one another in person.
Of course, there’s more to come than what I’ve shared here. We look forward to working with so many of you this year. If you’d like to raise your hand to get engaged, please email us at InvolveMe@FAIRInstitute.org.