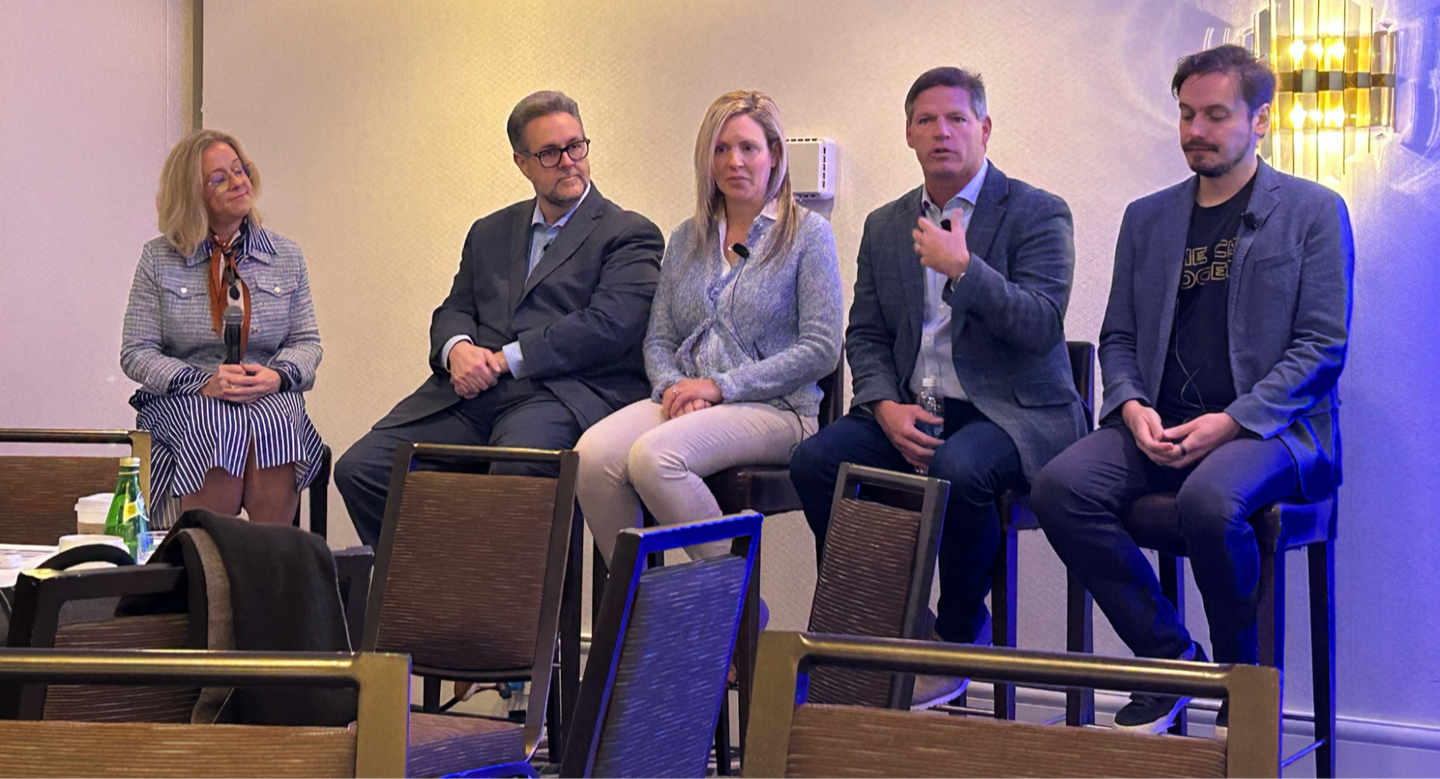
Expert Executive Panel from the FAIR Institute Breakfast Meeting during RSAC™ 2025 Conference.
In today's rapidly evolving threat landscape, cybersecurity has transcended its traditional role as a technical function to become a strategic business imperative. We convened a distinguished panel of security executives at the FAIR Institute Breakfast during the recent RSAC conference to share their experiences and insights on how organizations can effectively align cyber risk management with business objectives.
"Managing Risk at the Speed of Business"
Panelists:
>>Mark Tomallo, SVP, CISO, Victoria’s Secret
>>Alex Antukh, CISO, AboitizPower
>>Michelle Griffith, VP, Security Governance, Risk & Compliance. InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG)
>>Jonathan "JT" Taylor, Deputy CISO, UC Davis Health
>>Moderator: Bernadette Dunn, Head of Education, FAIR Institute
FAIR Institute Breakfast Meeting during RSAC 2025 Conference
Key Takeaways for Security Leaders
1. Start with business alignment: Understand your organization's strategic objectives and demonstrate how security initiatives support those goals, such as enhancing revenue generation, customer trust or operational efficiency.
2. Cultivate relationships: Build connections across the organization and develop security champions within business units. Collaborate closely with business unit leaders to find solutions that balance security requirements with operational needs.
3. Focus on impactful metrics: Prioritize measurements that directly connect to business outcomes and can drive decision-making. FAIR quantitative analysis gives a big boost here by aligning cyber risk management with the financial metrics the business knows well.
4. Embrace transparency: Be honest about uncertainty and limitations in risk assessments to build credibility with stakeholders. Again FAIR helps by communicating risk in terms of a range of probable outcomes.
5. Look beyond technology: While tools and automation are important, the most successful security programs balance technical controls with human expertise and organizational awareness.
Highlights of the Panel Discussion:
Business Enablement through Cyber Risk Programs: “Transform from Cost Centers to Value Creators”
The session began with an exploration of how cyber risk management programs can be aligned with broader business objectives to drive stakeholder engagement and support.
Mark Tomallo emphasized that successful alignment begins with understanding the organization's strategic priorities. "Cyber risk programs should be designed to protect what matters most to the business," he noted. "When security leaders can demonstrate how their initiatives directly support revenue generation, customer trust, or operational efficiency, they transform from cost centers to value creators."
The panelists agreed that effective communication is crucial for translating complex security concepts into business language. Storytelling emerged as a powerful tool for helping executives understand the implications of cyber risks. Rather than overwhelming stakeholders with technical details, successful CISOs frame security in terms of business impact, using real-world scenarios and case studies to illustrate potential consequences.
When discussing friction points, the panel acknowledged that resistance often stems from competing priorities and resource constraints. They suggested that security leaders can overcome these challenges by adopting a collaborative approach—working alongside business units to find solutions that balance security requirements with operational needs. Building relationships across departments and establishing security champions within business teams were highlighted as effective strategies for gaining broader organizational buy-in.
Data-Driven Decisions: “Connect to Business Outcomes”
The conversation then shifted to how metrics and reporting can drive informed business decisions.
Alex Antukh shared his perspective on key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most. "Effective cyber risk metrics should connect directly to business outcomes," he explained. "We focus on measuring time to detect and respond to incidents, vulnerability remediation rates, and the business impact of security incidents." He emphasized that contextualizing these metrics within industry benchmarks helps demonstrate progress and identify areas for improvement.
Mark Tomallo and JT provided compelling examples of how cyber risk data had influenced major business decisions. In one instance, a vulnerability assessment revealed significant risks associated with a proposed acquisition, leading to renegotiated terms that included remediation requirements before closing the deal. This example illustrated how security insights can protect business value beyond just preventing breaches.
Regarding the challenge of communicating uncertainty, the panelists advocated for transparency. They recommended using probability ranges rather than precise figures when reporting risks, and explicitly acknowledging limitations in data or analysis. This approach helps build credibility and ensures business leaders can make decisions with appropriate awareness of risks and confidence levels.
Third-Party & Vendor Risk Management (TPRM): Integrate Security into Procurement
As organizations increasingly rely on external partners, managing third-party cyber risks has become a critical component of security programs.
Michelle Griffith detailed her organization's approach to third-party risk management. "We begin by categorizing vendors based on the sensitivity of data they access and their criticality to our operations," she explained. "This enables us to apply appropriate levels of scrutiny during both initial assessments and ongoing monitoring." She emphasized the importance of integrating security requirements into procurement processes from the earliest stages to avoid retrofitting controls later.
JT contributed valuable insights on helping business owners understand the trade-offs between using third-party solutions versus internal capabilities. "Outsourcing doesn't eliminate risk—it transforms it," he noted. "Sometimes business leaders assume that using a vendor shifts all responsibility to that provider, but that's rarely the case." He recommended developing clear frameworks to help business stakeholders evaluate these decisions, considering factors beyond cost efficiency.
Mark added perspective on scaling challenges, noting that "as organizations grow, maintaining visibility across an expanding vendor ecosystem becomes increasingly complex." He stressed the importance of ensuring business owners understand this complexity when onboarding new vendors and the need to "put that risk back on the business to understand." The panel suggested that improvements in standardized assessment frameworks and greater information sharing across the industry could help address these challenges.
AI, Automation, and What's Next: Stay “Vigilant”
The final segment explored emerging technologies and their potential impact on cyber risk management.
JT offered a balanced view of AI's role in cybersecurity. "AI and machine learning are transforming our ability to detect patterns and anomalies that would be impossible to identify manually," he explained. "We're seeing promising applications in threat detection, vulnerability prioritization, and even predictive risk modeling." However, he cautioned that these technologies are not panaceas and require careful implementation and human oversight.
When discussing specific applications of AI in risk quantification, JT highlighted both opportunities and challenges. While AI can process vast amounts of data to identify correlations and potential risks, he noted that misuse of AI tools poses significant threats. "Organizations need to be particularly vigilant about how these technologies might be exploited by adversaries or lead to publicly embarrassing incidents if deployed without proper safeguards," he warned.
Looking ahead, the panel identified several technologies they believe will reshape cyber risk management in the coming years. These included advanced simulation capabilities for testing security controls, improved automation of security operations, and enhanced tools for visualizing complex risk landscapes.
Join the FAIR Institute - access our exclusive community of cyber and operational risk officers, cybersecurity leaders and business executives advancing quantitative measurement of risk. An individual membership is free - Join Now!