7 Bits of Advice on Scaling FAIR Risk Management to the Enterprise Level

We’re hearing increasingly that organizations successful at managing cyber risk in financial terms with Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR™) are now looking to enterprise risk management as the next frontier for quantitative risk management.
The enterprise risk management team at Rock Ventures (parent to Rocket Mortgage and other companies), a pioneer at applying FAIR to ERM, listed the benefits as:
- Focus primarily on revenue generation
- Always know future loss exposure and what is being done about it
- Compare different types of risk on an apples-to-apples basis
- Gain efficiencies from implementing consistent risk processes across the organization
To plan to extend the benefits of FAIR to ERM at your organization, consider these seven tips:


1. Introduce FAIR in the context of existing corporate philosophy
Cyber Risk Manager Cedric De Carvalho presented FAIR as furthering principles familiar to stakeholders in Richemont, such as “finding the right balance between agile business growth and protecting the business.” See the slides he shared in a FAIR Conference session here:
FAIR Use Case: Introducing Quantitative Risk Management at Fashion Group Richemont
2. Introduce FAIR with non-cyber risk scenarios
At Rock Ventures, “the team found that working with executives on analyzing potential mortgage default rates and other financial risk scenarios they already understood quite well made it easier to get buy-in for using FAIR modeling terminology, calibrated estimation methods, Monte Carlo simulation and other features in the ERM context.”
Case Study: Building a Rock-Solid ERM Culture on FAIR
3. Focus on business processes (and keep a low profile)
Also at Rock Ventures, “the team worked with the stakeholders and risk champions to decide which processes to measure first and, in some cases, to chain risk scenarios together (i.e., an effect on one asset is a threat to another) and identify potential root causes of risk in each scenario. The team endeavored to minimize its time demands on the business. Often, rather than scheduling meetings, risk specialists would temporarily embed themselves within a business process team and observe the team running its process.”
Case Study: Building a Rock-Solid ERM Culture on FAIR
4. Clean up the risk register
Risk registers can be dumping grounds for all kinds of nebulous concerns and one of the benefits of the FAIR approach is to re-cast risk register items into risk scenarios with a threat, asset, and effect so 1) they can be quantified in financial terms and 2) can be compared on a normalized basis across all the types of risk in enterprise risk management. Watch this:
Video: How to Turn Your Risk Register Items into Risk Scenarios You Can Quantify with FAIR
 Learn FAIR risk analysis - get certified as a FAIR expert through the FAIR Institute. See our online course offerings.
Learn FAIR risk analysis - get certified as a FAIR expert through the FAIR Institute. See our online course offerings.5. Use FAIR to comply with, and gain more from, enterprise risk standards and frameworks
Because FAIR defines risk scenarios consistently across the enterprise and provides a model to quantify risk in financial terms, it fills a need in the widely used COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework. The framework covers “what to do to incorporate risk into the definition and adjustment of business strategies, but when it comes to assessing risk and providing the data to inform those strategies- i.e., identifying, measuring, prioritizing, reporting risk - it does not provide any indication of how to do it.” FAIR can fill a similar role with NIST, ISO, GDPR and other standards and frameworks.
How FAIR Can Ensure the Success of COSO Risk Management Programs
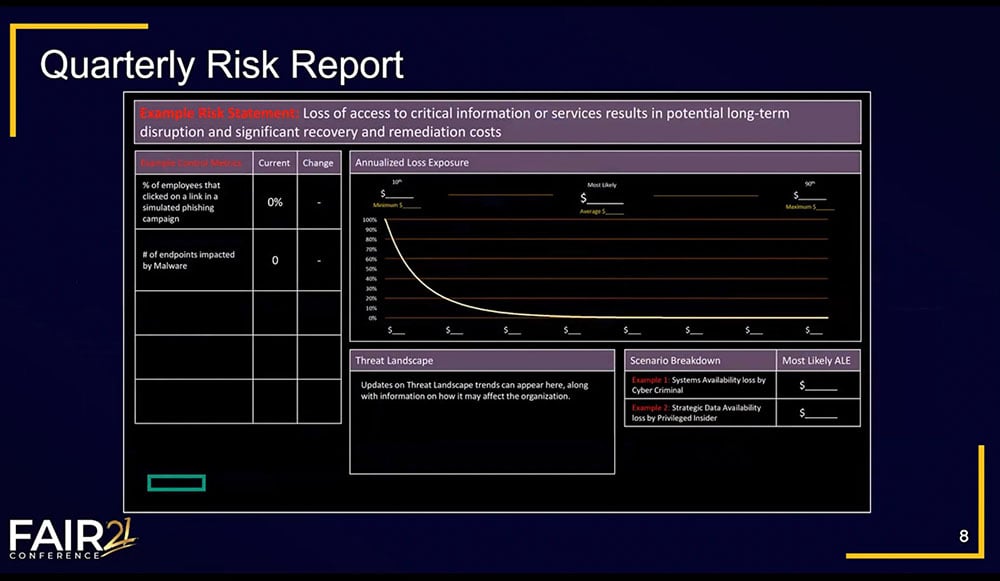
6. Use risk quantification to create a unified risk dashboard or reporting
At the 2021 FAIR Conference, HPE “showed examples (see above image) of quarterly risk reports, organized around five themes of highest concern for business leadership, that start with FAIR-formula risk statements, aggregate multiple quantitative analyses combined with indicators of effectiveness of the related controls, and reports on developments in the risk landscape for an all-around look at the risk theme.” HPE also is applying FAIR to operational risk for supply chain, IT, crisis management, product security and more. Watch a video of the HPE session:
How HPE Is Transitioning FAIR from Cyber to Enterprise Risk Management
7. Establish a governance model
“Establish the governance model that is best suited for the organization and your culture. A center of excellence (CoE) model is a common approach: the ERM unit sets the vision, establishes the ‘why’ and thus the types of information and the business questions to be answered, and supplies FAIR subject-matter experts but the individual operating units do the actual analysis. A more autocratic approach can work where the ERM units conduct the actual analysis, driving the operating units for the inputs but then reporting out the outputs. In the end, what matters is simply that the enterprise is better aware of the business risks, quantitatively measures the investment returns on the mitigations being proposed or implemented and understands where risk transfer (buying insurance or contract modification) is suitable.”